What is Operations Management - Definition & Guide
When you want to increase the efficiency of your business to its fullest potential, you need to administer a series of business practices and strategies to make it happen. This is done through operations management.
To set up an effective operations management team, you must utilize all of your company’s resources. Its most important resources include technology, equipment, materials and staff members. When you effectively use these resources every day in your organization, you will notice increased profitability and results.
As you read this article, you will learn more about operations management and why it is so important for a business to implement. Then you will learn how to put together good operations managers for your organization.
Here is what we'll be covering:
Operations Management Defined
Operations management is the management of your employees and resources. Every department of your business has a particular set of goals. For instance, Human Resources aims to hire qualified employees. Marketing teams aim to gain more sales and earn more profits for the company. You get the idea.
As for operations management, it is in charge of maximizing the efficiency of all your company’s resources. In other words, it wants to get the most out of your employees and resources in order to increase productivity for the company. This could mean having employees do more valuable work instead of repetitive work.
An operations manager might decide to use technology as a way to do the repetitive work. That way, employees can work on something more valuable with their time. These are the kinds of decisions that an operations manager must make.
The Job of an Operations Manager
There are so many different areas of an organization that are managed by operations managers. When you hire a chief operations officer, it is crucial that they have a diverse background in many of these areas, such as managing people, managing manufacturing operations, managing marketing, and so on.
A chief operations officer is a unique executive position because they are in charge of a cross-department, which is a department that works with several other different departments. Here is a basic rundown of their job description:
Map Out the Design of the Business Process
To achieve the goals of your business, map out each step that must be taken to achieve them. If you’re trying to complete a project for a client, then create a plan or timeline of steps from beginning to end. If you’re mapping out a business process to be implemented repeatedly, then create a structured procedure to increase the onboarding efficiency of your newest employees.
Basic Management
An operations manager performs basic management practices amongst all the departments. For instance, they create and improve their budgets, schedule maintenance work on equipment, and supervise employee behaviour and work practices.
Business Process Optimization
A lot of companies don’t like to bother improving their processes if they seem fine already. But if you check on your processes regularly, then you can always find ways to improve them. An operations manager is in charge of making processes more efficient, so it is important for them to be optimized as much as possible.

Do You Need Operations Management?
If you own a small business with a couple of employees, then you can manage all your processes just fine. On the other hand, if you’re managing a big company with more than 30 employees, then managing your processes becomes complicated. Your employees won’t know how to manage these processes by themselves.
Therefore, you need to create a list of standardized practices and procedures for your employees to follow. These practices will aim to increase efficiency in the workplace. Then you can enjoy a higher rate of output, higher profits, and a strong competitive advantage in your industry.
When an operations manager improves the processes of the organization, it means more products get produced with less defects. Whenever you have a higher output of better-quality products, it makes you stand out amongst the competition. This, in turn, is what leads to higher profits for you.
Business Process Management
You won’t find a lot of tutorials on operations management because it is comprised of several departments, such as Human Resources and Marketing. But if you understand business process management, then it will be easier to manage your operations.
As an operations manager, you should take the time to learn business process management. It is a practice where you evaluate, optimize, and automate your business processes. This must be a constant practice, so don’t think you can do it once and never again. It must be done regularly so that you can keep making continuous improvements to your processes.
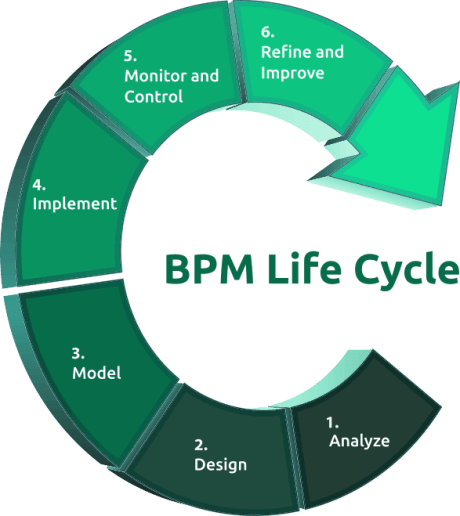
The lifecycle of business process management includes six steps:
- Analyze each business process for its effectiveness and optimization. Ensure that the process is aligned with the goals and objectives of the organization.
- Design some ideas for how to improve and optimize the process.
- Model how the changes would impact the process and the entire organization.
- Implement your new processes using software that allows you to easily create and edit them.
- Monitor and Control your processes to ensure that they are working properly.
- Refine and Improve your implementation continuously. A key part of BPM is to constantly look for ways to improve.
Business Process Reengineering
In some cases, it is a good idea to reengineer your business processes rather than make improvements to them. This means you’re starting over by recreating your business processes all over again from scratch.
Technology can simplify this task and make it easier. However, reengineering a process is more complicated than it sounds. Let’s look at Ford as an example.
Ford had an overstaffed accounts payable department with 500 employees, while Mazda only had 5 employees. Once Ford realized they were greatly underperforming, they started a business process reengineering campaign to find out why. What they discovered was the following:
- A purchase order is sent to the purchasing department. They send a copy of the order to the accounts payable department.
- Goods are sent to the material control department with a delivery document. The document is copied and sent to the accounts payable department.
- A receipt is sent to the accounts payable department by the vendor.
- Three different documents are compared and matched by the accounts payable department. Once the purchase is verified, the payment is sent by the department.
This entire process wastes so much time. Not only that, but it requires a lot of different employees to copy and send documents all day long. After Ford discovered why they were underperforming, the reengineered this business process. Document matching was no longer done manually. Instead, an online database was created where it could be done automatically.
As you can see, the operations manager has the power to improve business processes through business process reengineering.
The Six Sigma Method
Six Sigma is a management method to help reduce the number of defects in the manufacturing processes. Out of one million opportunities, you can’t have over 3.4 inadequacies or inefficiencies.
DMAIC is the most popular tool that is used to implement the Six Sigma method. It works to improve manufacturing processes in 5 easy steps:
Define – Measure – Analysis – Improvement – Control
- Define: Identify the problem with a particular manufacturing process and determine how it can be improved. Find the right tools or resources to use.
- Measure: Measure the performance of the process. This can help you figure how the best way to improve them.
- Analysis: What caused the issue with the process? Analyse it to find out.
- Improvement: Figure out the best possible solutions for the issue.
- Control: Start small when you implement each new process. Compare the results to the previous results to determine if things are getting better or not.
Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management is also important for operation managers to learn and implement. The growing complexity of organizations requires better supply chain management. Because of globalization, the flow of information, materials, and items goes through an international network of suppliers, companies, and end users. You can’t manage all of this without an efficient supply chain.
Operation managers have only been dealing with supply chain management since the 1990s. That is when globalization really took off in the United States and around the world. The purpose of supply chain management is to analyse every point of the product creation process, starting from its creation all the way to the time it’s sold to customers.
If you don’t understand your supply chain, then it could have a major impact on your company’s profitability and sales.
Operations Management Software
Software utilization is the best way to improve your business processes in operations management. If you try to improve processes manually, then you’re in for a world of hurt because your employees won’t know which practice to follow for a particular process. It is also time consuming and exhausting, especially when you try to track the metrics of these processes regularly.
Here are some more reasons why using operations management software is better:
- Easily design and create your processes using a drag and drop template designer.
- Refine and improve your processes. View previous versions of a process and revert back if required.
- Simplify your processes using powerful checklists.
- Display a wide range of information and collect an unlimited amount of data within your process checklists.
- Link checklists to simplify large processes. Start them automatically and link data within each process to further automate and simplify your workflow.
- Utilize other advanced workflow features, such as: Dynamic Due Dates, Halt Tasks and Conditional Logic to further customize your workflow.
- Collaborate easily by adding comments to tasks and mentioning other team members, or by assigning tasks to others.
- Access and complete your checklists on your mobile device.
- Automate and integrate with other apps.
- Monitor, manage and analyze your processes.
Hopefully, you have a good sense of why Operations Management Software is so much better. All your business processes can flow through CheckFlow, which can serve as your central hub. It lets you analyse each process and determine if delays exist. Then you will have an easier time optimizing and managing processes.
One of our most useful features for Operations Management is our Real-Time Dashboard. This allows you to monitor all of your processes from one screen. It is updated automatically and in real-time. As soon as a task has been completed your dashboard will be updated without needing to refresh. As an Operations Manager you can sit back and easily track your processes.
You can see a demo of our dashboard being updated in real-time below,
Check out our home page for more details.